 The pediatrician just informed you that your child is profoundly deaf.
The pediatrician just informed you that your child is profoundly deaf.
What is deafness like?
How does deafness impact a person’s life? What will you do now? Your answers to these questions will depend on personal experience. If you have connections to Deaf culture, you may feel very differently than someone who has never had interacted with a deaf person. Though we live in the Information Age, mainstream society still understands very little about what it means to be deaf.
This week, Nick News with Linda Ellerbee premiered an episode titled “Now Hear This!” (watch the full episode HERE ) The show does a great job exploring the spectrum of deafness, and demystifying the deaf experience by telling the stories of 5 deaf young people. The children’s’ experiences are vastly diverse, and touch on a number of issues from deaf education methods to family dynamics. The overall message is that, like any of us, deaf children have individual needs. Despite what some may claim, there is no one-size-fits-all strategy for being deaf!
S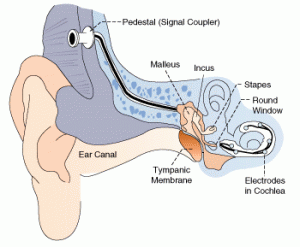 ome families choose to assimilate their child to a hearing lifestyle by implanting a device called a cochlear implant into the skull, which stimulates the auditory nerve and allow the brain to “hear.” Sammy is a CI recipient from a hearing family who jokingly refers to herself as “part robot.” She was not born deaf, but her hearing deteriorated throughout childhood and, at 12 years old, she made the choice to have CI surgery. According to Sammy, her parents presented the pros and cons, and she strongly feels a CI was the right choice for her. She attends school with all other hearing students and plays on a basketball team, insisting she doesn’t need to know ASL because she can hear. Cici also comes from a hearing family, she lost her hearing as a baby. Her parents elected to send her to a school for deaf children that focuses on teaching English and oral communication, so she never learned any ASL. At 5 years old she received her CI. “It was hard to learn to speak,” she says, but she feels very grateful that she did because it allows her to communicate with her family and non-deaf friends. Cici is a ballet and tap dancer who feels that deafness is a disability that her CI and hearing aid help her overcome.
ome families choose to assimilate their child to a hearing lifestyle by implanting a device called a cochlear implant into the skull, which stimulates the auditory nerve and allow the brain to “hear.” Sammy is a CI recipient from a hearing family who jokingly refers to herself as “part robot.” She was not born deaf, but her hearing deteriorated throughout childhood and, at 12 years old, she made the choice to have CI surgery. According to Sammy, her parents presented the pros and cons, and she strongly feels a CI was the right choice for her. She attends school with all other hearing students and plays on a basketball team, insisting she doesn’t need to know ASL because she can hear. Cici also comes from a hearing family, she lost her hearing as a baby. Her parents elected to send her to a school for deaf children that focuses on teaching English and oral communication, so she never learned any ASL. At 5 years old she received her CI. “It was hard to learn to speak,” she says, but she feels very grateful that she did because it allows her to communicate with her family and non-deaf friends. Cici is a ballet and tap dancer who feels that deafness is a disability that her CI and hearing aid help her overcome.
Although the first instinct of a hearing parent might be to “fix” their “disabled” child through technology, they should first explore the many perspectives about deafness. Yes, cochlear implants and hearing aids work great for some people, but every person is different and everyone learns differently. In the show, CiCi says she loves her CI, but acknowledges how difficult it was to learn spoken English. Imagine having dyslexia– or any common learning disability– and being forced to learn a challenging foreign language. Though Cochlear Implants or oral English education do work for many, it’s unfair to assume that all deaf children have the same capabilities.
Other families choose American Sign Language for their deaf child. Isabella was born deaf and grew up in an all-ASL family, with two deaf parents and one hearing sister. She discusses education at her Deaf school, playing soccer on a hearing team, and having fierce Deaf pride! Isabella does not view deafness as a disability in any way, and she loves the language of her family. Arbab is a young man from a hearing family, who became deaf as an infant. In Pakistan, he would not have had educational opportunities, so his family immigrated to the US to ensure a better life. Arbab’s family does not use ASL and he does feel isolated from them, but he absolutely loves attending Deaf school where he signs freely with his peers. He uses technology, such as texting or video chat, to contact his friends when he is feeling lonely. Kaylee is the only deaf person in her entire town but, when she was in preschool, school administrators decided to add ASL to the curriculum for her whole class. The hearing kids all learned sign language, and use it throughout the school day to make sure Kaylee feels included. “My hearing friends sign to me, they are very fluent,” she says, “when my hearing friends don’t sign to me, then I feel alone.” She and her hearing friends love ASL and have made it their goal to spread Deaf awareness by volunteering to teach ASL to children.
As a parent, it is your responsibility to become educated about your child; to engage and develop a relationship with them. Learn about deafness, and Deaf culture. Discover all the options available before making any major life decisions. Deaf children, like hearing children, have limitations, and areas where they excel. Instead of dictating how young deaf people should live their lives, parents can work together with their child to find the most comfortable way of adapting. This solution may not always be what the parent initially expected, and that’s ok! Holding on to strict expectations for any child– deaf or hearing– is unfair. Every person and their circumstances are unique!
“Now Hear This!” explores a spectrum of deafness, language use, and the various strategies deaf people use to communicate. We get a glimpse of how deaf people fit into different families, and how much parental choices can impact the course of a child’s life. Most importantly, the program presents 5 well-adjusted young people doing the best they can to learn new things, make new friends, and be understood “in a hearing world that doesn’t listen.”

















 Cycle 22 of “America’s Next Top Model” premiered on August 5 and one contestant, Nyle DiMarco, really captured viewers’ attention. Not only is he charming and (as
Cycle 22 of “America’s Next Top Model” premiered on August 5 and one contestant, Nyle DiMarco, really captured viewers’ attention. Not only is he charming and (as  According to a
According to a  Over the past few years, we have seen a small number of deaf/HoH personalities get the chance to shine on reality TV. Actress Marlee Matlin made it all the way to the final episode of “The Celebrity Apprentice,” raising over a million dollars for charity. On hit CBS show “The Amazing Race,” Deaf competitor Luke Adams traveled the world conquering many challenges and ultimately securing third place. Kurt “the Irish Chef” Ramborger was the first Deaf contestant on Food Network’s “Chopped.”
Over the past few years, we have seen a small number of deaf/HoH personalities get the chance to shine on reality TV. Actress Marlee Matlin made it all the way to the final episode of “The Celebrity Apprentice,” raising over a million dollars for charity. On hit CBS show “The Amazing Race,” Deaf competitor Luke Adams traveled the world conquering many challenges and ultimately securing third place. Kurt “the Irish Chef” Ramborger was the first Deaf contestant on Food Network’s “Chopped.” In 2013, Deaf designer Justin LeBlanc was given the opportunity to show his skills on “Project Runway,” proving a fierce competitor to the very end. Christy Smith became the first Deaf contestant on “Survivor,” and went on to star in her own PBS show called “Christy’s Kids: Challenge Yourself.” Nina Poersch, another deaf contestant, competed on “Survivor: Worlds Apart.” Season 4 of “The Janice Dickienson Modeling Agency” featured Martin Ritchie, a model who happens to be deaf. And in 2011, mtvU (an MTV channel) premiered a short reality show called “Quiet Campus” which documented life at Gallaudet University, the only liberal arts college in the world designed specifically for deaf students.
In 2013, Deaf designer Justin LeBlanc was given the opportunity to show his skills on “Project Runway,” proving a fierce competitor to the very end. Christy Smith became the first Deaf contestant on “Survivor,” and went on to star in her own PBS show called “Christy’s Kids: Challenge Yourself.” Nina Poersch, another deaf contestant, competed on “Survivor: Worlds Apart.” Season 4 of “The Janice Dickienson Modeling Agency” featured Martin Ritchie, a model who happens to be deaf. And in 2011, mtvU (an MTV channel) premiered a short reality show called “Quiet Campus” which documented life at Gallaudet University, the only liberal arts college in the world designed specifically for deaf students. The success of shows with non-traditional characters, such as “Orange is the New Black,” “Daredevil,” and “Switched at Birth” underscores a major shift in pop culture paradigm. Audiences are finally holding the media accountable for showing America as a country of all colors, cultures, and abilities. Viewers are seeking new characters and perspectives, and they are
The success of shows with non-traditional characters, such as “Orange is the New Black,” “Daredevil,” and “Switched at Birth” underscores a major shift in pop culture paradigm. Audiences are finally holding the media accountable for showing America as a country of all colors, cultures, and abilities. Viewers are seeking new characters and perspectives, and they are  Imagine this: you sit down on Sunday evening to stream a popular TV program– that show everyone will be discussing tomorrow. When the show starts, however, all the characters are using a completely foreign language. You can’t understand a thing! There are no subtitles and no closed captioning. Everyone on your Twitter feed is chatting about the program, but you aren’t able to follow the plot! This frustrating scenario is common for people who are Deaf or hard of hearing. Media technology is rapidly evolving, yet accessibility continues to lag behind.
Imagine this: you sit down on Sunday evening to stream a popular TV program– that show everyone will be discussing tomorrow. When the show starts, however, all the characters are using a completely foreign language. You can’t understand a thing! There are no subtitles and no closed captioning. Everyone on your Twitter feed is chatting about the program, but you aren’t able to follow the plot! This frustrating scenario is common for people who are Deaf or hard of hearing. Media technology is rapidly evolving, yet accessibility continues to lag behind. The 9th Circuit Federal appeals court recently ruled that
The 9th Circuit Federal appeals court recently ruled that  It is estimated that one in every six people on Earth experiences some degree of hearing loss; that number grows to one in three for individuals over 65 years old. These are people who deserve the same access to new media and pop culture as everyone else, and closed captioning helps provide that. Closed captioning doesn’t just serve individuals who are Deaf/HoH, closed captioning is helpful for those with autism and intellectual developmental disorders, making it easier to follow along with the video. Additionally, many closed captioning users are non-native speakers who utilize the text to help learn the spoken language. Have you ever tried to watch a sports game in a noisy bar? This is an example where closed captioning is helpful for everyone.
It is estimated that one in every six people on Earth experiences some degree of hearing loss; that number grows to one in three for individuals over 65 years old. These are people who deserve the same access to new media and pop culture as everyone else, and closed captioning helps provide that. Closed captioning doesn’t just serve individuals who are Deaf/HoH, closed captioning is helpful for those with autism and intellectual developmental disorders, making it easier to follow along with the video. Additionally, many closed captioning users are non-native speakers who utilize the text to help learn the spoken language. Have you ever tried to watch a sports game in a noisy bar? This is an example where closed captioning is helpful for everyone. The first closed captioning appeared on PBS stations in 1972, more than 20 years after hearing Americans had come to rely on TV as a source of news and entertainment. During this turbulent time in American history, television was forming culture and shaping public opinion, but Deaf individuals had to seek out this information in other ways. In 1979 the National Captioning Institute was created to work with TV networks to provide closed captioning, which was only available if the viewer purchased an expensive set-top decoder box: a barrier for many people. The Television Decoder Circuitry Act was passed in 1990, giving the Federal Communications Commission oversight of closed captioning. The Television Decoder Circuitry Act required almost all television receivers sold or manufactured have the built-in ability to display closed captioning by July 1, 1993. This act was later expanded upon to include regulations for digital television sets.
The first closed captioning appeared on PBS stations in 1972, more than 20 years after hearing Americans had come to rely on TV as a source of news and entertainment. During this turbulent time in American history, television was forming culture and shaping public opinion, but Deaf individuals had to seek out this information in other ways. In 1979 the National Captioning Institute was created to work with TV networks to provide closed captioning, which was only available if the viewer purchased an expensive set-top decoder box: a barrier for many people. The Television Decoder Circuitry Act was passed in 1990, giving the Federal Communications Commission oversight of closed captioning. The Television Decoder Circuitry Act required almost all television receivers sold or manufactured have the built-in ability to display closed captioning by July 1, 1993. This act was later expanded upon to include regulations for digital television sets. It took over a decade for the FCC to begin regulating Internet broadcast.
It took over a decade for the FCC to begin regulating Internet broadcast.  While certain online companies scramble to catch up, or make excuses for not providing adequate captioning, other entities are embracing the opportunity to break down communication barriers. Apple is one company that has gone above and beyond to welcome diverse users. By creating products with excellent built-in accessibility, and providing outstanding accessibility support, Apple really sets the bar for inclusion. Kickstarter recently launched it’s new video captioning initiative with the tag line “creativity is for everyone.” Kickstarter is one of the largest crowdfunding sites on the web; countless individuals have had their projects funded by other people around the world using this platform. By making it easy for people who are deaf to access these opportunities, Kickstarter helps open the door for future deaf innovators and entrepreneurs.
While certain online companies scramble to catch up, or make excuses for not providing adequate captioning, other entities are embracing the opportunity to break down communication barriers. Apple is one company that has gone above and beyond to welcome diverse users. By creating products with excellent built-in accessibility, and providing outstanding accessibility support, Apple really sets the bar for inclusion. Kickstarter recently launched it’s new video captioning initiative with the tag line “creativity is for everyone.” Kickstarter is one of the largest crowdfunding sites on the web; countless individuals have had their projects funded by other people around the world using this platform. By making it easy for people who are deaf to access these opportunities, Kickstarter helps open the door for future deaf innovators and entrepreneurs. The pediatrician just informed you that your child is profoundly deaf.
The pediatrician just informed you that your child is profoundly deaf. ome families choose to assimilate their child to a hearing lifestyle by implanting a device called a cochlear implant into the skull, which stimulates the auditory nerve and allow the brain to “hear.” Sammy is a CI recipient from a hearing family who jokingly refers to herself as “part robot.” She was not born deaf, but her hearing deteriorated throughout childhood and, at 12 years old, she made the choice to have CI surgery. According to Sammy, her parents presented the pros and cons, and she strongly feels a CI was the right choice for her. She attends school with all other hearing students and plays on a basketball team, insisting she doesn’t need to know ASL because she can hear. Cici also comes from a hearing family, she lost her hearing as a baby. Her parents elected to send her to a school for deaf children that focuses on teaching English and oral communication, so she never learned any ASL. At 5 years old she received her CI. “It was hard to learn to speak,” she says, but she feels very grateful that she did because it allows her to communicate with her family and non-deaf friends. Cici is a ballet and tap dancer who feels that deafness is a disability that her CI and hearing aid help her overcome.
ome families choose to assimilate their child to a hearing lifestyle by implanting a device called a cochlear implant into the skull, which stimulates the auditory nerve and allow the brain to “hear.” Sammy is a CI recipient from a hearing family who jokingly refers to herself as “part robot.” She was not born deaf, but her hearing deteriorated throughout childhood and, at 12 years old, she made the choice to have CI surgery. According to Sammy, her parents presented the pros and cons, and she strongly feels a CI was the right choice for her. She attends school with all other hearing students and plays on a basketball team, insisting she doesn’t need to know ASL because she can hear. Cici also comes from a hearing family, she lost her hearing as a baby. Her parents elected to send her to a school for deaf children that focuses on teaching English and oral communication, so she never learned any ASL. At 5 years old she received her CI. “It was hard to learn to speak,” she says, but she feels very grateful that she did because it allows her to communicate with her family and non-deaf friends. Cici is a ballet and tap dancer who feels that deafness is a disability that her CI and hearing aid help her overcome.




